|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| api | ||
| config | ||
| core | ||
| env | ||
| errs | ||
| job | ||
| logger | ||
| models | ||
| opm | ||
| period | ||
| pool | ||
| runtime | ||
| tests | ||
| utils | ||
| ca.crt | ||
| config_test.yml | ||
| config.yml | ||
| generateCerts.sh | ||
| main.go | ||
| README.md | ||
| server.crt | ||
| server.key | ||
Job Service
Job service is designed to handle and process the asynchronous background jobs with an easy way. It is built on top of gocraft/work job queue framework with supporting
- Fast and efficient.
- Reliable - don't lose jobs even if your process crashes.
- If a job fails, it will be retried a specified number of times.
- Schedule jobs to happen in the future.
- Enqueue unique jobs so that only one job with a given name/arguments exists in the queue at once.
- Periodically enqueue jobs on a cron-like schedule.
and the following additional capabilities:
- Rest API.
- Execution context.
- More job status:
error,success,stopped,cancelledandscheduled. - More controllable actions:
stopandcancel. - Enhanced periodical jobs.
- Status web hook.
Use cases
With job service, you can:
- Submit a
Genericjob which will be executed immediately if worker resource is available and can be only execute once. - Submit a
Scheduledjob which will be executed after a specified delay. - Submit a
Periodicjob which will be repeatedly executed with specified interval. - Submit job with
uniqueflag to make sure no duplicated jobs are executing at the same time. - Stop a specified job.
- Cancel a specified job.
- Retry a specified job (This should be a failed job and match the retrying criteria).
- Get stats of specified job (no list jobs function).
- Get execution log of specified job.
- Check the health status of job service.
Architecture
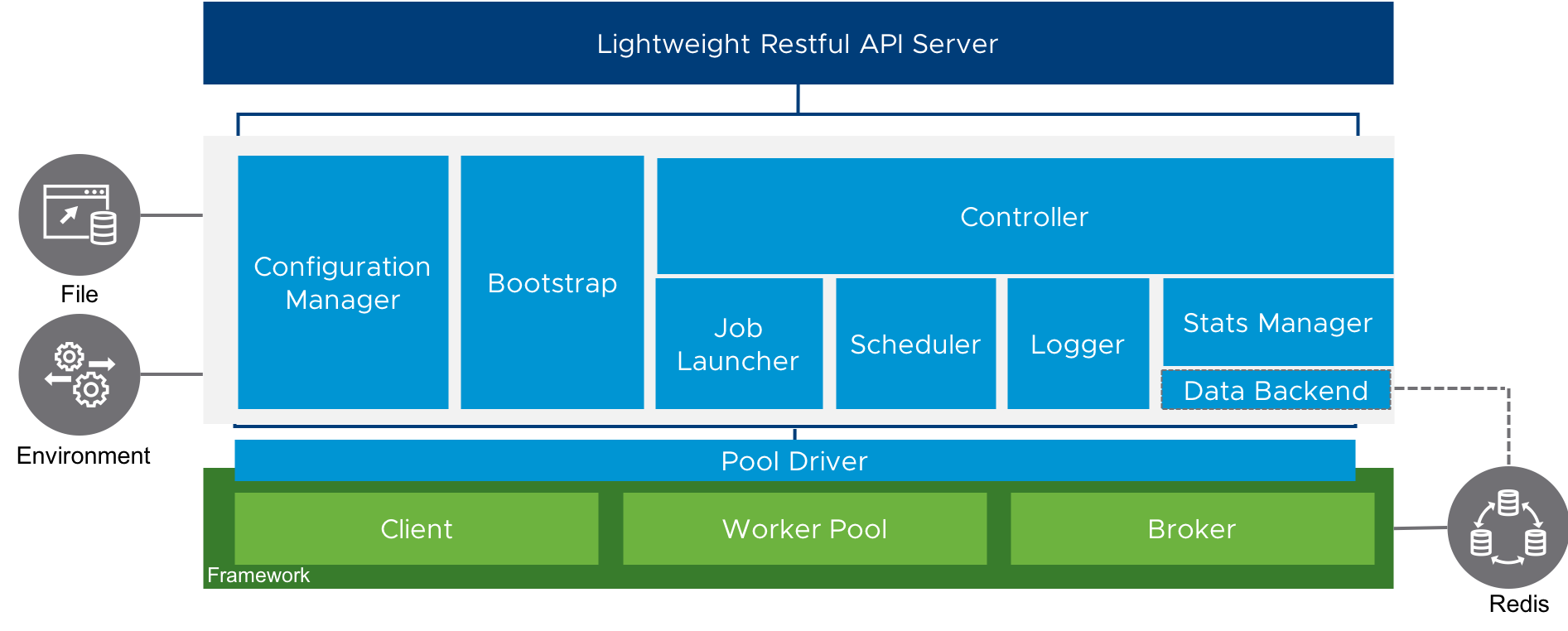
The overall architecture of the job service is shown in the below graph:
Components:
- API Server: A go lightweight restful API server to serve the related restful requests.
- Configuration Manager: Responsible for handing the configurations used in job services. Two sources supported: yaml file and env variables.
- Bootstrap: Take the responsibilities to initialize related context and start API server and worker pool. The main start point of job service.
- Controller: The core of job service. Responsible for coordinating the whole flow of job service.
- Job Launcher : Launch the jobs except
Periodicones. - Scheduler: Schedules the
Periodicjobs. - Logger: Catches and write the job execution logs to files.
- Stats Manager: Maintains the status and stats of jobs as well as status hooks.
- Data Backend: Define storage methods to store the additional info.
- Pool Driver: A interface layer to broke the functions of upstream job queue framework to upper layers.
- Persistent driver: So far, only support
redis.
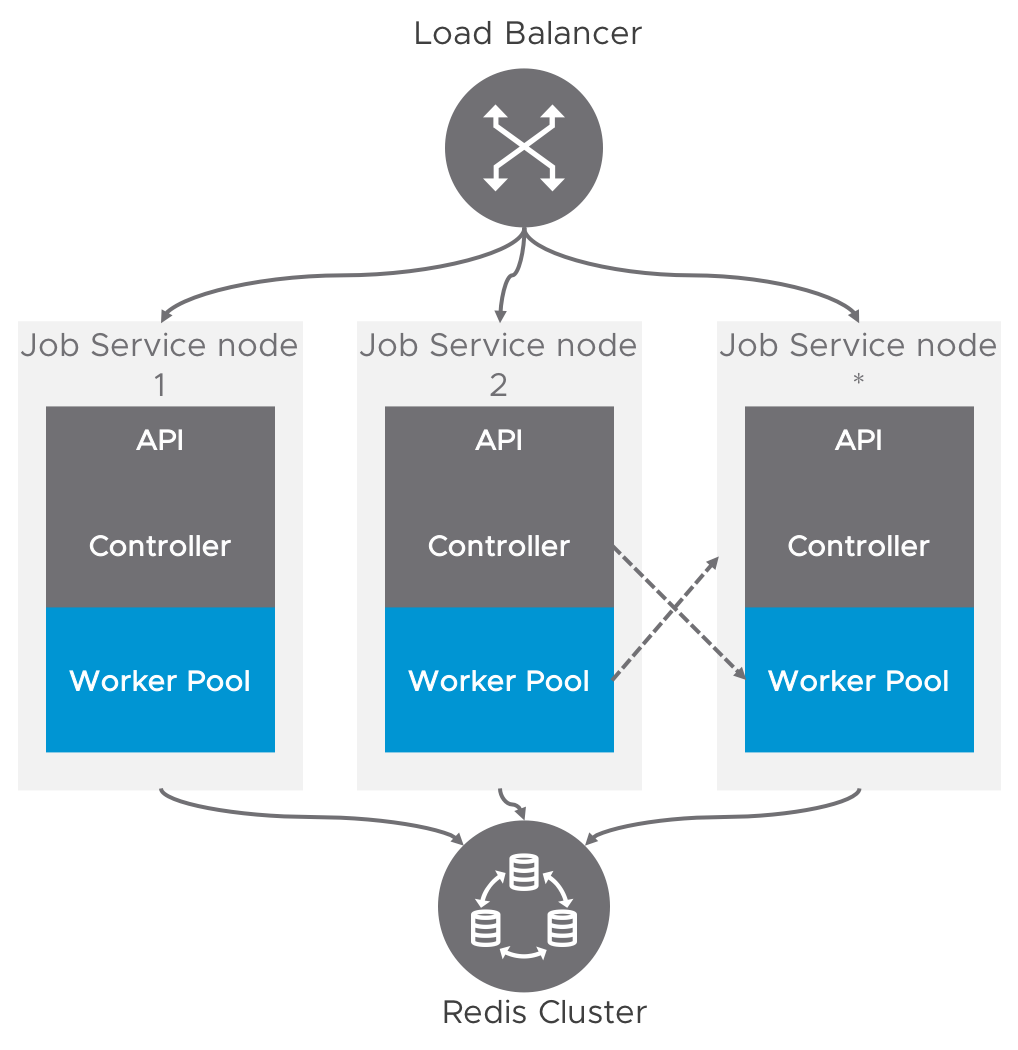
Currently, the worker (compute node) and controller (control plane) are packaged in one process. To achieve scalability and HA functionality, multiple nodes can be deployed under a LB layer.
As described in above graph, the controller and work pool which are located in different nodes can also talk to each other via a virtual channel - the backend persistent driver. That means the job enqueued by a controller may be selected by other worker pool which is located in another node.
Programming Model
To let the job service recognize the job, the implementation of job should follow the programming model.
Job Interface
A valid job must implement the job interface. For the details of each method defined in the job interface, you can refer the comments attached with the method.
// Interface defines the related injection and run entry methods.
type Interface interface {
// Declare how many times the job can be retried if failed.
//
// Return:
// uint: the failure count allowed. If it is set to 0, then default value 4 is used.
MaxFails() uint
// Tell the worker pool if retry the failed job when the fails is
// still less that the number declared by the method 'MaxFails'.
//
// Returns:
// true for retry and false for none-retry
ShouldRetry() bool
// Indicate whether the parameters of job are valid.
//
// Return:
// error if parameters are not valid. NOTES: If no parameters needed, directly return nil.
Validate(params map[string]interface{}) error
// Run the business logic here.
// The related arguments will be injected by the workerpool.
//
// ctx env.JobContext : Job execution context.
// params map[string]interface{} : parameters with key-pair style for the job execution.
//
// Returns:
// error if failed to run. NOTES: If job is stopped or cancelled, a specified error should be returned
//
Run(ctx env.JobContext, params map[string]interface{}) error
}
Just pay attention, your main logic should be written in the Run method.
Job Context
A job context will be provided when executed the Run logic. With this context, you can
- Get a logger handle if you want to output the execution log to the log file.
- Retrieve the system context reference.
- Get job operation signal if your job supports
stopandcancel. - Get the
checkinfunc to check in message. - Get properties by key
- Specified to harbor, db connection and all the configurations can be retrieved by context.
Cancellable Job
To make the job cancellable, some special logic should be coded in the Run logic.
First, check the signal at certain execution points,
if cmd, ok := ctx.OPCommand(); ok {}
Then, check if it is a cancel signal,
if cmd == opm.CtlCommandCancel {}
finally, if it is, exit the logic and return the cancel error.
return errs.JobCancelledError()
Stoppable Job
To make the job stoppable, some special logic should be coded in the Run logic.
First, check the signal at certain execution points,
if cmd, ok := ctx.OPCommand(); ok {}
Then, check if it is a stop signal,
if cmd == opm.CtlCommandStop {}
finally, if it is, exit the logic and return the cancel error.
return errs.JobStoppedError()
Check In Message
If you want to report more concrete status info, just call the Checkin function in the job context like the below code piece shown:
ctx.Checkin("30%")
Job Implementation Sample
Here is a demo job:
// DemoJob is the job to demostrate the job interface.
type DemoJob struct{}
// MaxFails is implementation of same method in Interface.
func (dj *DemoJob) MaxFails() uint {
return 3
}
// ShouldRetry ...
func (dj *DemoJob) ShouldRetry() bool {
return true
}
// Validate is implementation of same method in Interface.
func (dj *DemoJob) Validate(params map[string]interface{}) error {
if params == nil || len(params) == 0 {
return errors.New("parameters required for replication job")
}
name, ok := params["image"]
if !ok {
return errors.New("missing parameter 'image'")
}
if !strings.HasPrefix(name.(string), "demo") {
return fmt.Errorf("expected '%s' but got '%s'", "demo steven", name)
}
return nil
}
// Run the replication logic here.
func (dj *DemoJob) Run(ctx env.JobContext, params map[string]interface{}) error {
logger := ctx.GetLogger()
defer func() {
logger.Info("I'm finished, exit!")
fmt.Println("I'm finished, exit!")
}()
fmt.Println("I'm running")
logger.Info("=======Replication job running=======")
logger.Infof("params: %#v\n", params)
logger.Infof("context: %#v\n", ctx)
if v, ok := ctx.Get("email_from"); ok {
fmt.Printf("Get prop form context: email_from=%s\n", v)
}
if u, err := dao.GetUser(models.User{}); err == nil {
fmt.Printf("u=%#+v\n", u)
}
/*if 1 != 0 {
return errors.New("I suicide")
}*/
// runtime error
// var runtime_err error = nil
// fmt.Println(runtime_err.Error())
logger.Info("check in 30%")
ctx.Checkin("30%")
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
logger.Warning("check in 60%")
ctx.Checkin("60%")
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
logger.Debug("check in 100%")
ctx.Checkin("100%")
time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)
// HOLD ON FOR A WHILE
logger.Error("Holding for 20 sec")
<-time.After(15 * time.Second)
// logger.Fatal("I'm back, check if I'm stopped/cancelled")
if cmd, ok := ctx.OPCommand(); ok {
logger.Infof("cmd=%s\n", cmd)
fmt.Printf("Receive OP command: %s\n", cmd)
if cmd == opm.CtlCommandCancel {
logger.Info("exit for receiving cancel signal")
return errs.JobCancelledError()
}
logger.Info("exit for receiving stop signal")
return errs.JobStoppedError()
}
fmt.Println("I'm close to end")
return nil
}
Configuration
The following configuration options are supported:
| Option | Description | ENV variable |
|---|---|---|
| protocol | Protocol used to serve http | JOB_SERVICE_PROTOCOL |
| https_config.cert | The tls cert if enabled https protocol | JOB_SERVICE_HTTPS_CERT |
| https_config.key | The tls key if enabled https protocol | JOB_SERVICE_HTTPS_KEY |
| port | API server listening port | JOB_SERVICE_PORT |
| worker_pool.worker_pool | The worker concurrency number | JOB_SERVICE_POOL_WORKERS |
| worker_pool.backend | The job data persistent backend driver. So far, only redis supported | JOB_SERVICE_POOL_BACKEND |
| worker_pool.redis_pool.redis_url | The redis url if backend is redis | JOB_SERVICE_POOL_REDIS_URL |
| worker_pool.redis_pool.namespace | The namespace used in redis | JOB_SERVICE_POOL_REDIS_NAMESPACE |
| logger.path | The file path to keep the log files | JOB_SERVICE_LOGGER_BASE_PATH |
| logger.level | Log level setting | JOB_SERVICE_LOGGER_LEVEL |
| logger.archive_period | The days to sweep the outdated logs | JOB_SERVICE_LOGGER_ARCHIVE_PERIOD |
| admin_server | The harbor admin server endpoint which used to retrieve Harbor configures | ADMINSERVER_URL |
Sample
---
#Protocol used to serve
protocol: "https"
#Config certification if use 'https' protocol
https_config:
cert: "server.crt"
key: "server.key"
#Server listening port
port: 9443
#Worker pool
worker_pool:
#Worker concurrency
workers: 10
backend: "redis"
#Additional config if use 'redis' backend
redis_pool:
#redis://[arbitrary_username:password@]ipaddress:port/database_index
#or ipaddress:port[,weight,password,database_index]
redis_url: "redis:6379"
namespace: "harbor_job_service"
#Logger for job
logger:
path: "/Users/szou/tmp/job_logs"
level: "INFO"
archive_period: 1 #days
#Admin server endpoint
admin_server: "http://10.160.178.186:9010/"
API
Authorization
As job service is always running in the backend environment, a simple secret auth way is choose now. To call the job service API, the Authorization header must be appended.
Authorization : Harbor-Secret <secret>
The expected secret is passed to job service by the ENV variable CORE_SECRET.
Endpoints
POST /api/v1/jobs
Submit jobs
- Request body
{
"job": {
"name": "demo",
"parameters": {
"p1": "just a demo"
},
"status_hook": "https://my-hook.com",
"metadata": {
"kind": "Generic", // or "Scheduled" or "Periodic"
"schedule_delay": 90, // seconds, only required when kind is "Scheduled"
"cron_spec": "* 5 * * * *", // only required when kind is "Periodic"
"unique": false
}
}
}
-
Response
- 202 Accepted
{ "job": { "id": "uuid-job", "status": "pending", "name": "DEMO", "kind": "Generic", "unique": false, "ref_link": "/api/v1/jobs/uuid-job", "enqueue_time": "2018-10-10 12:00:00", "update_time": "2018-10-10 13:00:00" } }- 401/500 Error
{ "code": 500, "err": "short error message", "description": "detailed error message" }
GET /api/v1/jobs/{job_id}
Get job stats
-
Response
- 200 OK
{ "job": { "id": "uuid-job", "status": "pending", "name": "DEMO", "kind": "Periodic", "unique": false, "ref_link": "/api/v1/jobs/uuid-job", "enqueue_time": 1539164886, "update_time": 1539164886, "run_at": 1539164986, "cron_spec": "* 5 * * * * ", "check_in": "check in message", // if check in message "check_in_at": 1539164889, // if check in message "die_at": 0, "hook_status": "http://status-check.com" } }- 401/500 Error
{ "code": 500, "err": "short error message", "description": "detailed error message" }
POST /api/v1/jobs/{job_id}
Stop/Cancel/Retry job
- Request body
{
"action": "stop" //or "cancel" or "retry"
}
-
Response
- 204 No content
- 401/404/500/501 Error
{ "code": 500, "err": "short error message", "description": "detailed error message" }
GET /api/v1/jobs/{job_id}/log
Retrieve job log
-
Response
- 200 OK
Log text bytes
- 401/400/404/500 Error
{ "code": 500, "err": "short error message", "description": "detailed error message" }
GET /api/v1/stats
Check job service healthy status
-
Response
- 200 OK
[{ "worker_pool_id": "pool1", "started_at": 1539164886, "heartbeat_at": 1539164986, "job_names": ["DEMO"], "concurrency": 10, "status": "healthy" }]- 401/500 Error
{ "code": 500, "err": "short error message", "description": "detailed error message" }
How to Run
It's easy to run the job service.
- First, compile and build the binary
// under jobservice folder
go build -a -o jobservice
-
Second, create configuration yaml file and configure the job service.
-
Then, export the secret via ENV variable
CORE_SECRET. -
Finally, start the service with the following command,
jobservice -c <config_yaml_file_path>
Enjoy it!